Bernoulli's principle 3d animation
Channel: Bifrost
Category: Education
Tags: compressible flow in fluid dynamicsbernoulli equationkinetic energyhyperphysicnon-conductingtypes of flowconservation of energyfluid's potential energybernoulli's principleincompressible flowspotential energyanimation3dderivations of the bernoulli equationdynamic pressureliquidphysics (field of study)internal energydaniel bernoullihydrodynamicaincompressible flow equationsimplified formgasesinviscid flow
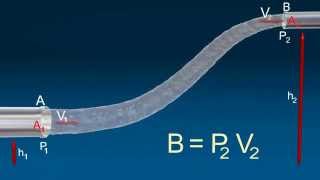
Description: Bernoulli's principle 3d animation This is an important principle involving the movement of a fluid through a pressure difference. Suppose a fluid is moving in a horizontal direction and encounters a pressure difference. This pressure difference will result in a net force, which by Newton's 2nd law will cause an acceleration of the fluid. The fundamental relation,which is known as Bernoulli's principle. This is very similar to the statement we encountered before for a freely falling object, where the gravitational potential energy plus the kinetic energy was constant (i. e., was conserved). Bernoulli's principle thus says that a rise (fall) in pressure in a flowing fluid must always be accompanied by a decrease (increase) in the speed, and conversely, if an increase (decrease) in , the speed of the fluid results in a decrease (increase) in the pressure. This is at the heart of a number of everyday phenomena. As a very trivial example, Bernouilli's principle is responsible for the fact that a shower curtain gets ``sucked inwards'' when the water is first turned on. What happens is that the increased water/air velocity inside the curtain (relative to the still air on the other side) causes a pressure drop. The pressure difference between the outside and inside causes a net force on the shower curtain which sucks it inward. A more useful example is provided by the functioning of a perfume bottle: squeezing the bulb over the fluid creates a low pressure area due to the higher speed of the air, which subsequently draws the fluid up. This is illustrated in the following figure.