Pharmacology – ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS (MADE EASY)
Channel: Speed Pharmacology
Category: Education
Tags: antifungal agentsechinocandin mechanism of actionpharmacology made easyantifungal treatmentazoles mechanism of actionallylamines mechanism of actionamphotericin b pharmacologyamphotericin bfungal cell wallantifungal drugs عبد المتعالfungal cell structureazoles pharmacologyechinocandinsantifungal drugs pharmacologyantifungal drugspharmacology antifungalsazole antifungalsantifungal agents pharmacologyantifungals pharmacology
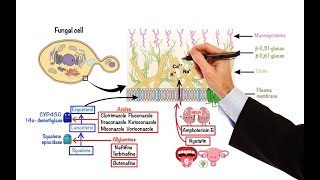
Description: Antifungals are a class of drugs used for the treatment of systemic and superficial fungal infections. Most antifungal drugs interfere with ergosterol biosynthesis, bind to ergosterol to disrupt fungal cell membrane integrity, or target enzymes involved in cell wall construction. Based on their mechanism of action, the major agents can be grouped into five classes: Polyenes (Amphotericin B, Nystatin); Allylamines (Naftifine, Terbinafine); Azoles (Clotrimazole, Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Ketoconazole, Miconazole, Voriconazole); Echinocandins (Anidulafungin, Caspofungin, Micafungin) and other agents such as Griseofulvin and Flucytosine. Thanks for watching and don't forget to SUBSCRIBE, hit the LIKE button👍 and click the BELL button🔔 for future notifications!!! Like what we do? Learn how to support us on Patreon! 💪patreon.com/speedpharmacology 00:00 Intro - Fungal cell wall 01:17 Amphotericin B and Nystatin 02:53 Azoles and Allylamines 04:41 Echinocandins 05:47 Griseofulvin and Flucytosine




















